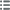
正面
正面的文字 LVD. XIIII. D. G. (MM) - FR. ET. NAV. REX.
正面的说明书 Buste juvénile de Louis XIV à droite, les cheveux longs, lauré, drapé et cuirassé ; au-dessous (Mg).
正面的翻译 (Louis XIV, par la grâce de Dieu, roi de France et de Navarre).
背面
背面的文字 SIT. NOMEN. DOMINI - & - BENEDICTVM. 1679.
背面的说明书 Écu de France couronné.
背面的翻译 (Béni soit le nom du Seigneur).
评论
历史细节
LOUIS XIV "THE SUN KING"
(05/14/1643-09/01/1715)
The reign of Louis XIV is the longest and most glorious in the history of France. Son of Louis XIII and Anne of Austria, born September 5, 1638, the third Bourbon king ascended the throne in 1643 and remained there for seventy-three years. He died on September 1, 1715, aged seventy-seven.. Between 1643 and 1661, under the regency of Anne of Austria and the ministry of Cardinal Mazarin, absolutism was built through combat: internal struggle against the Fronde, external struggle against Spain. The personal reign of Louis XIV began in 1661, when the young king decided to "govern by himself".. The absolute monarchy then reached its peak, the king being surrounded by a team of exceptional ministers: Le Tellier, Louvois, Colbert, Seignelay. This prosperous period ended during the 1680s, with the first setbacks, the revocation of the Edict of Nantes (1685), the end of the great external successes and the gradual disappearance of the entourage of the first years (Colbert died in 1683 , Le Tellier in 1685, Seignelay in 1690, Louvois in 1691). The third and last part of the reign, between 1685 and 1715, is more difficult. The aging king finds no such collaborators. Glorious, this reign was first a warlike reign. Never has France known so many wars: the Thirty Years' War, completed with the Empire in 1648, with Spain only in 1659, War of Devolution (1667-1668), War of Holland (1672-1678), war with Spain (1684), War of the League of Augsburg (1688-1697), War of the Spanish Succession (1701-1713). She never knew more victories and more conquests: in 1648, the treaties of Westphalia gave her Alsace, in 1659, the peace of the Pyrenees, Artois and Roussillon; in 1668, by the Peace of Aix-la-Chapelle, it reached Flanders; in 1678, by the Treaty of Nijmegen, Franche-Comté. In 1681, the king annexed Strasbourg. The following decades were less happy: in 1697 (Treaty of Ryswick), France ceded Luxembourg; in 1713 and 1714 (treaties of Utrecht and Rastadt), she abandoned Acadia, a prelude to the loss of America, fifty years later. The reign of Louis XIV therefore corresponds quite exactly to the age of French preponderance in Europe: France supplanted Spain; it will soon be supplanted by England, which holds the empire of the seas and the expanses of the New World. To the glory of the victorious and conquering king is added the glory of the king administrator, legislator, protector of arts and letters. Louis XIV and his ministers gave perfection to the construction of the monarchy: the legislation was reformed, the nobility subdued, the provinces tamed, heresy overthrown, artists and writers put themselves at the service of royal power. Lex una sub uno sole: "a single law under a single sun": everything must revolve around the star-master. The whole of Europe feels the attraction and prestige of Versailles. The reality is undoubtedly less brilliant than this flattering program: the royal administration remains too small to really frame the largest and most populous kingdom in Europe; particularisms resist; the Protestants leave to enrich the enemies of France. The fact remains that it is the image of the king of glory that has imposed itself in the memories, as Louis XIV had decided and wanted it.. There lies the true triumph of this prince: for France and for Europe, for the following century and for centuries to come, for contemporaries as for posterity, he was and remains the king par excellence.. Coins and medals, which restore to us the Jupiterian profile of the great monarch, are part of this will and this success.. Louis XIV paid particular attention to them: the Grand Siècle is also a great century of numismatics.








 对产品描述纠错
对产品描述纠错 打印
打印 分享我的选择
分享我的选择 提问
提问 Consign / sell
Consign / sell
 产品介绍
产品介绍










