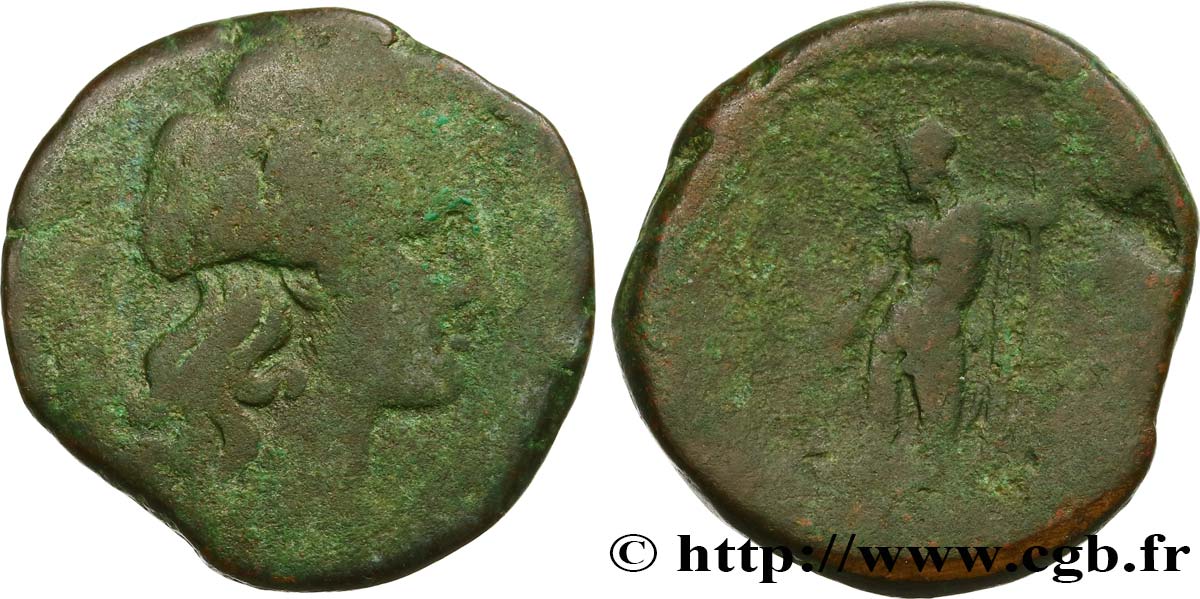
正面
正面的文字 ANÉPIGRAPHE.
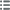
正面的说明书 Tête laurée d’Apollon à droite ; une lyre derrière la tête.
背面
背面的说明书 Guerrier (Arès) nu debout à gauche, casqué, la chlamyde sur l’épaule, tenant une épée dans son fourreau de la main droite et une longue javeline de la main gauche, appuyé sur son bouclier.
背面铭文 [MAMERTINWN/ P]
背面的翻译 (des Mamertins).
历史细节
SICILY - MESSANA
(288-38 BC)
The Mamertini
Messina was founded by the Chalcidians around 725 BC. -VS. under the name of Zancle (sickle), a name that comes from the shape of the port of the city. The Samiens, fleeing the Persian yoke, seized the city in 493 BC.. -VS. and kept it for four years, until Anaxilas, tyrant of Rhegion, drove them out and renamed the city Messina.. Anaxilas and his son were overthrown in 461 BC. -VS. and established democracy. It was destroyed by the Carthaginians in 396 BC.. -VS. The city was rebuilt at the instigation of Dionysius the Elder. After the death of Dionysius, the city took part in the rivalries which saw Dion and Dionysius the Younger confront each other.. A tyrant favorable to the A Carthaginians took power and held it until the arrival of Timoleon in Sicily. Messina, after regaining some prosperity during the second half of the 4th century BC. -VS. , was still the object of the lusts of Agathokles from 315 BC. -VS. After the death of the king, the city was once again ravaged by a new invader, this time Oscan mercenaries who destroyed the city and massacred its inhabitants in 288 BC.. -VS. The new masters, the Mamertines, maintained their autonomy under the control of the Romans until the 1st century BC.. -VS. Pyrrhus seized the city on arriving in Sicily, but could not control the Mamertines who, after a brief return to Italy, returned to Sicily and tried to carve out a vast territory before being crushed at the battle of Langanos by Hieron II in 269-265 BC. -VS. The Carthaginians saved the Mamertines and Messina. But the latter allied with the Romans and it was the siege of Messina by the Carthaginians and the Syracusans which was at the origin of the first Punic war (264-241 BC).. -VS. ). Messina kept its status as an allied city at the end of the conflict.. It prospered during the Roman period thanks to its geographical and strategic location of its port, a link between the continent and the island.. During the civil wars (49-31 BC. -VS. ), Messina supported Caesar against Pompey then Sextus Pompey against Octave and Marc Antoine until the defeat of Nauloque in 36 BC. -VS.








 对产品描述纠错
对产品描述纠错 打印
打印 分享我的选择
分享我的选择 提问
提问 Consign / sell
Consign / sell
 产品介绍
产品介绍















