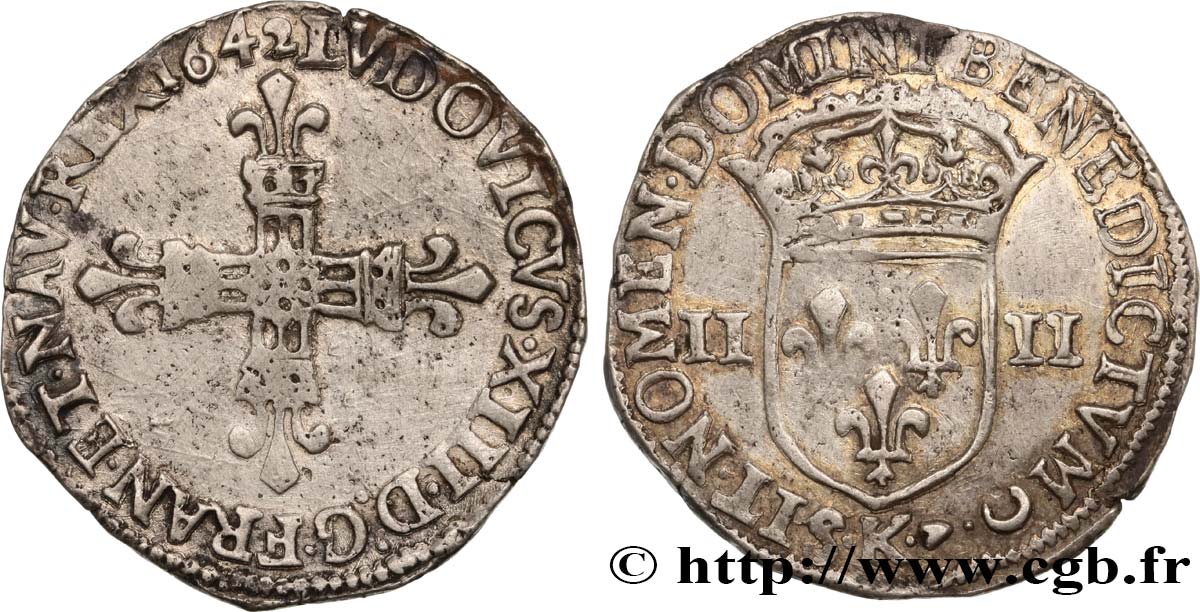
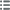
正面
正面的文字 LVDOVICVS. XIII. D: G. FRAN. ET. NAV. REX 1642.
正面的说明书 Croix fleurdelisée avec quadrilobe en cœur.
正面的翻译 (Louis XIII, par la grâce de Dieu, roi de France et de Navarre).
背面
背面的文字 SIT. NOMEN. DOMINI. BENEDICTVM (MG). (MM) - K, (LÉGENDE COMMENÇANT À 6 HEURES).
背面的说明书 Écu de France couronné et accosté de II, II ; lettre d'atelier à la pointe de l'écu.
背面的翻译 (Béni soit le nom du Seigneur).
历史细节
LOUIS XIII
(05/14/1610-05/14/1643)
Son of Henri IV and Marie de Médicis, Louis XIII was born in Fontainebleau in 1601. King in 1610, he reigned first under the regency of his mother, who followed a policy of conciliation with Spain and showered the Great with favors to ensure their peace.. The Estates General, meeting in 1614-1615, showed the disunity of the Orders and the impossibility of financial reforms. The favorite of the regent, Concino Concini, marquis of Ancre, was at the head of affairs until 1617, date of his assassination by order of the king.. The new favourite, Albert de Luynes, received the dignity of constable and governed until his death before Montauban in 1621, continuing a foreign policy favorable to the Habsburgs.. Returning to power, the queen-mother brought one of her creatures, Richelieu, former bishop of Luçon, into the Council.. From 1626 and until the end of the reign, Richelieu was as Prime Minister the absolute master of the State.. The successive plots of Marie de Medici, Gaston d'Orléans, Anne of Austria and Cinq-Mars could not overcome the favor of the cardinal. He submitted the Protestant party (taking of La Rochelle, 1628, edict of grace of Alès, 1629) and brought France into the Thirty Years' War, a war first covered (1630) then open (1635). This long enterprise of "lowering the House of Austria" was to last until 1659.. Richelieu did not see the end of it, but was able to attend the conquest of Artois, Alsace and Roussillon. With the 1630s, came a "revolution in the art of governing" corresponding to the ministry of Richelieu and the entry of France into the Thirty Years' War.. In the context of the "military revolution" of the 17th century (tenfold increase in numbers, preponderance of infantry and firearms, bastioned fortification), the unprecedented war effort imposed and justified an all-powerful state, driven by sole reason of state. "Giant of the great century", studied by the Anglo-Saxons more than by the historians of France, the French army became an armed Leviathan; the tax that feeds her weighed like never before. The exercise of power gained in efficiency, with the organization of the Council of State and the institution of intendants. A first control of opinion and language was put in place (institution of the French Academy, creation of the Gazette de France). Power also tended towards brutality: evoking the early 1630s, Omer Talon writes that "we wanted things by authority and not by concert". The Fronde appears as a failed reaction to these too rapid changes. Warrior king, king imbued with his duties, Louis XIII let the Grand Cardinal do everything while retaining the direction of the armies, which he led with bravery (siege of La Rochelle, 1628, affair of Pas de Suse, 1629, conquest of Roussillon, 1642). He used Richelieu without liking him, but after his death in 1642 he retained his ministers and continued his policy until his death the following year.. From Anne of Austria married in 1614, he had two sons, Louis XIV and Philippe d'Orléans.








 对产品描述纠错
对产品描述纠错 打印
打印 分享我的选择
分享我的选择 提问
提问 Consign / sell
Consign / sell
 产品介绍
产品介绍















