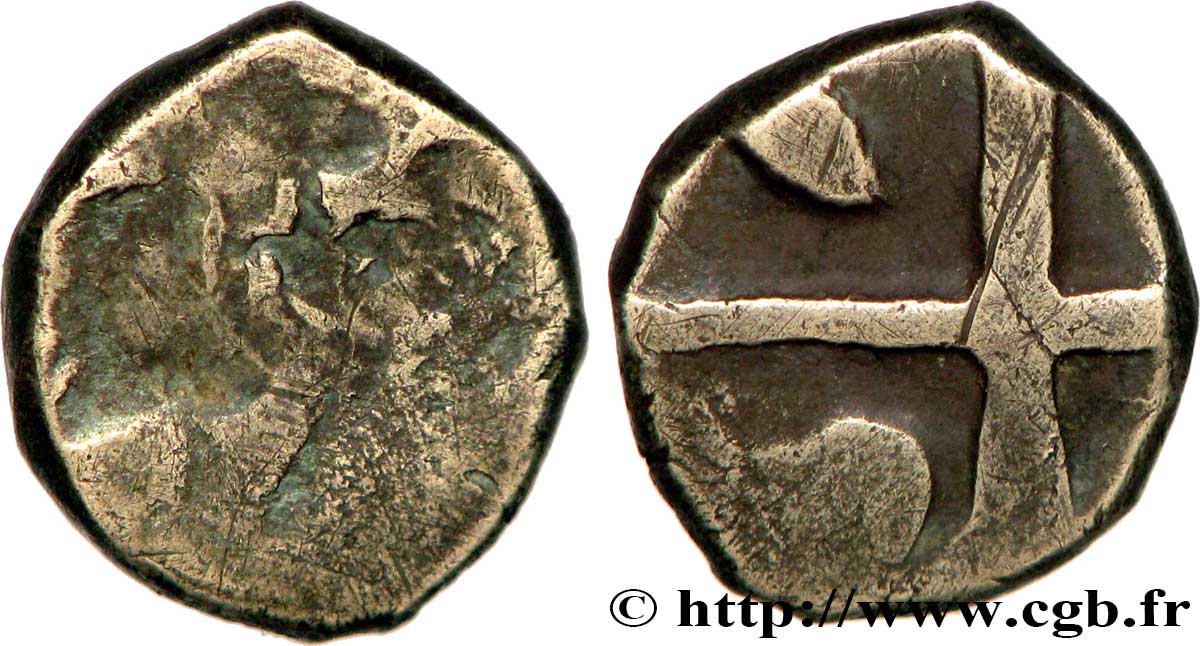
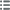
正面
正面的文字 ANÉPIGRAPHE.
正面的说明书 Lisse, avec des motifs informes.
背面
背面的文字 ANÉPIGRAPHE.
背面的说明书 Croix formée de quatre cantons ornés chacun d'une lunule : une hache au 3e canton.
评论
历史细节
GALLIA - SOUTH WESTERN GAUL - VOLCÆ TECTOSAGES (Area of Toulouse)
(2nd - 1st century BC)
The people of the Volques Tectosages (people who seek a roof) are one of the three main components of the Galatians who ravaged Greece and Asia Minor between 281 and 277 BC. -VS. Legend has it that the Volques Tectosages who migrated to Languedoc participated in the sack of Delphi and seized part of the treasures of the temple of Apollo at Delphi (at the origin of the gold of the Tectosages "aurum Tolosanum" ) and transported it to Tolosates (Vieille-Toulouse), their capital. In fact, the Volques Tectosages would come from Bohemia and would have emigrated during the 3rd century AD.. They nevertheless took part in the Danubian expeditions which led the Celts to the coasts of the Aegean, the Bosphorus and the Black Sea.. Mercenaries, they served the Carthaginians during the Punic Wars and were perhaps at the origin of the revolt of the mercenaries which almost took the Phoenician colony. From the Danube, they passed into Cisalpine Gaul (Italy) where they enlisted as mercenaries and are better known under the name of Gesates before passing into Gaul and settling in the South-West, in Aquitaine. The Volques Tectosages were certainly the most powerful people of Aquitaine. Quintus Servilius Cæpio who crushed the Volque coalition in 105 BC. -VS. would have seized "the gold of Toulouse", fruit of the plundering of the temple of Apollo of Delphi that the Tectosages would have repatriated with them before installing it in Tolosa. To have seized this treasure, he would then have known only misfortune! Sources: Cicero (Pro Fonteio 12), Caesar (BG. VI, 24), Strabo (G. IV, 1 and 13), Pliny (HN. III, 33), Ptolemy (G. II, 10), Kruta (71-72, 250-251, 253, 262, 265, 268, 275, 302-304, 306-307, 309-310, 323, 338, 343, 349, 376, 763, 865 ).








 对产品描述纠错
对产品描述纠错 打印
打印 分享我的选择
分享我的选择 提问
提问 Consign / sell
Consign / sell
 产品介绍
产品介绍













