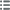
正面
正面的文字 MIRE. ANT. FR. FERRAND. MRE. DES. REQ. INTEND. EN. BOVRG. ET. BRESSE.
正面的说明书 Armes couronnées et soutenues par deux licornes.
背面
背面的文字 LA. VILLE. DE. DIJON. ; À L’EXERGUE : 1701.
背面的说明书 Armes de Dijon.
评论
历史细节
DIJON (MAYORS OF ... and miscellaneous)
The city of Dijon had a mayor and in general twenty municipal magistrates or aldermen from the time of the birth of feudalism.. These magistrates are confirmed in 1187, when a Charter of commune is granted by the duke Hugues III. At the end of the 13th century, this mayor took the title of viscount mayor, confirmed in 1477-1479 by Louis XI, which he kept until 1789.. Since the end of the 15th century (1491), the office of Viscount Maïeur has been ennobling as well as that of alderman from the 16th century.. The Viscount Maïeur had the right of high, medium and low justice, the right of seal and visit. The keys of the city are entrusted to him and he directs the archers as well as the companies of the seven districts, this military function being important until the XVIIth century. Elective function, the Viscount Maïeur is elected by the inhabitants, neither beggars nor foreigners, who pay the size, generally on the eve of Saint John. From 1669, he was allowed to wear “a long robe of full satin, violet in color, lined with crimson red satin, like the provost of the merchants of Lyon, with a hood of the same fabric and color edged with ermine” in order to to stand out from the locals. In 1692, the function of Viscount Maïeur was created as a hereditary office while the election was no longer a confirmation of the royal choice made by the governor in the name of the king.. Represented on the seals, the Viscount Maïeur then had his arms appear on the tokens from 1553, then his initials quickly replaced by his title and name.. These tokens are originally intended to make the accounts which indicate quite well the legends of the first tokens POR CAMERA COMPOTORUM CITY, For the chamber of accounts of the city then PRO RATION REDD. URB. DIVISION. , For the accountability of the city of Dijon. They quickly become a payment for the right of presence as can be the rights of spices, candles, etc.. . At the end of the 17th century, silver tokens appear in this series and we can assume that their function is now only representative.. Bibliography: Collection of engraved plates from the collection of tokens from the towns and mayors of Dijon, Beaune and Auxonne, from the cabinet of C. -NOT. Amanton, Dijon, 1824 (printed at 20 ex. ) and edition of Henri Baudot and F. Rabut according to Ferdinand Amanton, Historical and chronological summary of the establishment of the commune and of the viscount mayors or mayors of Dijon, on the attributions assigned to these magistrates and on the established practice of striking tokens during the administration of each of them, published in the Memoirs of the Antiquities Commission of the Côte-d'Or, Volume VIII, 1870-1873.










 对产品描述纠错
对产品描述纠错 打印
打印 分享我的选择
分享我的选择 提问
提问 Consign / sell
Consign / sell
 产品介绍
产品介绍









