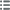
正面
正面的文字 ANÉPIGRAPHE.
正面的说明书 Tête à droite, la chevelure bouclée.
背面
背面的文字 ANÉPIGRAPHE.
背面的说明书 Bige à droite, une victoire ailée au-dessus et trois annelets entre les jambes.
评论
历史细节
GALLIA - BITURIGES CUBI (Area of Bourges)
(2nd - 1st century BC)
The Bituriges Cubes were one of the most powerful peoples of the Celtic. Their territory extended over part of Bourbonnais, Touraine and Berry, the current departments of Cher, Indre and part of Allier. Their capital was the oppidum of Avaricum (Bourges). The Loire separated them from the Aedui and the Carnutes. They also had for neighbors the Pictons, the Lémovices and the Arvernes. According to the account of Livy, the king of Bituriges, Ambigat would have reigned over the whole of unified Gaul in the 6th century BC.. -VS. and would have sent his two nephews, Bellovèse and Sigovèse, one to Italy, the other to the East, to found the Gallic Empire which, a century later, extended over Great Britain, central Europe (except Switzerland), northern Italy and most of the Danube. Before the Gallic Wars, the Bituriges would have been the clients of the Aedui and a contingent of Boii would have been installed on their territory.. Their main wealth came from animal husbandry and iron mining which had brought them wealth and prosperity.. In 52 BC. -VS. , they supported Vercingetorix. They were defeated at Genabum (Orleans) by Caesar. Vercingetorix encouraged them to practice the scorched earth technique. They thus destroyed more than twenty oppida, but refused the same fate to their capital, Avaricum (Bourges). Caesar came to besiege the oppidum, defended by thirty thousand Bituriges and ten thousand allies. The city was taken and burned, only eight hundred soldiers were able to escape, while the garrison and the population were massacred.. Caesar found there abundant reserves which enabled him to spend the winter and prepare the campaign for the following spring.. Nevertheless, the Bituriges would still have provided a contingent of twelve thousand men to the relief army of the Gallic coalition, during the siege of Alésia. At the beginning of 51 BC. -VS. , Caesar led a new campaign among the Bituriges who submitted very quickly. A few weeks later, they intervened with Caesar to fight against the Carnutes. Caesar (BG. I, 18; VII, 5, 8, 9, 11-13, 15, 21, 29, 75, 90, VIII, 2, 3, 4, 11). Strabo (G. IV, 2). Livy (HR. V, 34, 35). Pliny (HN. , IV. 109). Ptolemy (G. II, 7). Kruta: 68-70, 145, 186-187, 212-213, 240, 334, 344, 360.








 对产品描述纠错
对产品描述纠错 打印
打印 分享我的选择
分享我的选择 提问
提问 Consign / sell
Consign / sell
 产品介绍
产品介绍









